|
About "Lectin"
|
[Discovery, 발견]
In 1888, Peter Hermann Stillmark of Estonia discovered a protein component (hemagglutinin) that agglutinates red blood cells from the seeds of the plant castor bean (Ricinus communis), and this molecule was named "ricin".1) In the early 1900s, Japanese Hideyo Noguchi also found lectins in the venom of pit vipers and discovered limulin as an invertebrate lectin from horseshoe crabs.2,3)
1888년, 에스토니아의 Peter Hermann Stillmark는 피마자(Ricinus communis) 씨앗에서 적혈구를 응집시키는 단백질 성분(혈구응집소, hemagglutinin)을 발견하였으며, 이 분자를 리신(ricin)이라 명명하였습니다. 1900년대 초반, 일본의 노구치 히데요(Hideyo Noguchi)는 살무사(pit viper)의 독에서 렉틴(lectin)을 발견하였으며, 투구게(horseshoe crab)에서 무척추동물 렉틴인 리물린(limulin)을 발견하였습니다.
[Nomenclature, 명명법]
The term "lectin" was coined in 1954 by William C. Boyd and Elizabeth Shapleigh, based on the Latin words "lego/legere" (to read, choose, or gather) and the suffix "-in", which denotes proteins, to describe substances from plants that show blood group-specific agglutination of red blood cells.4)
"렉틴(lectin)"이라는 용어는 1954년 William C. Boyd와 Elizabeth Shapleigh에 의해 처음 명명되었습니다. 이는 라틴어 lego/legere (읽다, 선택하다, 모으다)와 단백질을 의미하는 접미사 -in이 결합된 형태로, 식물 유래 물질 중 혈액형 특이적 적혈구 응집 활성을 나타내는 물질을 의미합니다.
[Definition, 정의]
In 1980, Irwin J. Goldstein, R. Colin Hughes, Michel Monsigny, Toshiaki Osawa, and Nathan Sharon defined lectins as "carbohydrate-binding proteins that have the ability to agglutinate cells or precipitate polysaccharides and glycoproteins, and are not immune response products (antibodies)".5)
While some lectins cannot agglutinate cells due to a lack of multivalent binding sites, other molecules, such as glycosyltransferases, glycosidases, carbohydrate-related transporters and kinases, can agglutinate cells. In 1981, Jan Kocourek and Václav Hořejší proposed a broader definition of lectins as "carbohydrate-binding proteins that do not modify the sugars they bind to".6,7) Lectins are often classified based on carbohydrate-binding specificity or gene family, reflecting species differences and a wide range of functions.8)
1980년, Irwin J. Goldstein, R. Colin Hughes, Michel Monsigny, Toshiaki Osawa, Nathan Sharon은 렉틴을 "세포를 응집시키거나 다당류 및 당단백질을 침전시키는 능력을 가지며, 면역반응 산물(항체)이 아닌 탄수화물-결합 단백질" 과 같이 정의하였습니다. 다만, 일부 렉틴은 다가 결합 부위(multivalent binding site)가 없어 세포 응집이 일어나지 않을 수 있으며, 반면 당전이효소(glycosyltransferase), 당가수분해효소(glycosidase), 탄수화물 관련 수송체 및 키나아제 등의 다른 분자들은 세포 응집 기능을 가질 수도 있습니다. 이에 따라, 1981년 Jan Kocourek과 Václav Hořejší는 기존 정의를 확장하여 렉틴을 "렉틴은 결합하는 당을 변형시키지 않는 탄수화물-결합 단백질"과 같이 재정의하였습니다. 렉틴은 탄수화물 결합 특이성 또는 유전자 계통(gene family)에 따라 분류되며, 이는 생물 종(species) 간의 차이와 다양한 기능성을 반영합니다.
[Applications, 응용]
Inspired by the differences in agglutination reactions of red blood cells from different animals toward various lectins, Karl Landsteiner discovered the human ABO-type blood group (glycan antigens) in 1900 and he won the Nobel Prize in 1930.9) Lectins have long been used for analyzing and profiling the distinct surface glycans of different cells. Recently, technologies such as "lectin microarray-based glycan profiling" and "DNA barcode-labeled lectin single-cell glycan analysis" have been developed, making lectins crucial in cutting-edge research on cell surface glycans.10,11)
적혈구 응집 반응의 차이에 대한 연구를 바탕으로, Karl Landsteiner는 1900년 **인간 ABO 혈액형(당항원, glycan antigens)**을 발견하였으며, 1930년 노벨 생리학·의학상을 수상하였습니다.
이후 렉틴은 세포 표면 당쇄(glycan) 분석 및 프로파일링에 지속적으로 활용되어 왔습니다. 최근에는 렉틴을 활용한 렉틴 마이크로어레이 기반 당쇄 프로파일링(lectin microarray-based glycan profiling), DNA 바코드-표지 렉틴 단일세포 당쇄 분석(DNA barcode-labeled lectin single-cell glycan analysis)과 같은 최신 분석 기술이 개발되어, 렉틴이 세포 표면 당쇄 연구의 필수적인 도구로 자리 잡고 있습니다.
|
Products
|
Hemagglutinin Lectin (Recombinant lectins)
R0225 Recombinant Polyporus squamosus lectin (= rPSL1a) expressed in Escherichia coli
R0226 Recombinant Laetiporus sulphureus lectin N-Terminal Domain (= rLSL-N) expressed in Escherichia coli
R0227 Recombinant Marasmius oreades agglutinin (= rMOA) expressed in Escherichia coli
R0228 Recombinant Sclerotium rolfsii lectin (= rSRL) expressed in Escherichia coli
R0229 Recombinant Griffithsia sp. lectin (= rGRFT) expressed in Escherichia coli
L0169 Lectin, Fucose specific (= AOL) from Aspergillus oryzae (5mg/mL, PBS pH6.5)
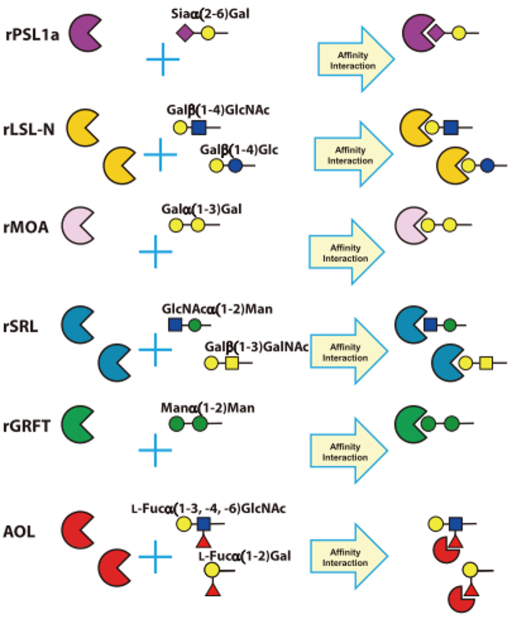
Product No. R0225, R0226, R0227, R0228, R0229 were commercialized under license from National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Japan.
Product No. L0169 was commercialized under license from GEKKEIKAN SAKE COMPANY, LTD.
|
Applications
|
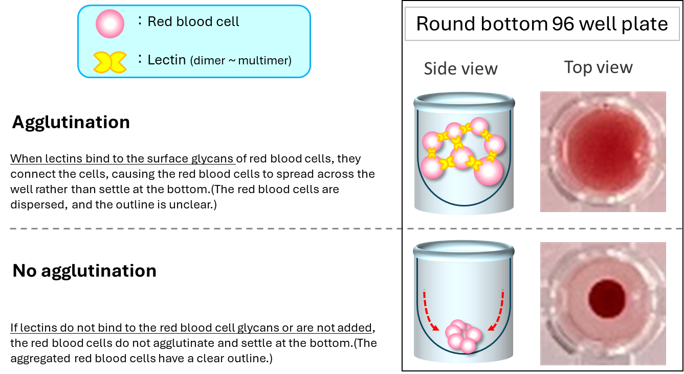
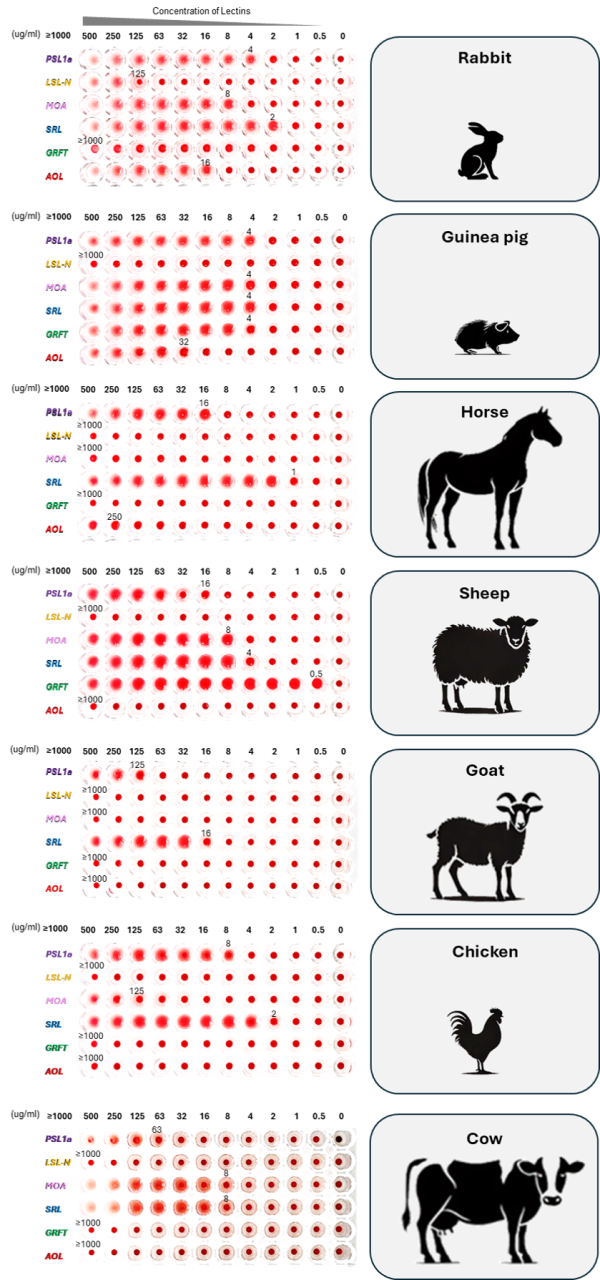
The differences in the cellular glycans of animal red blood cells can be easily observed with our lectin series.
TCI의 렉틴 시리즈를 사용하면 다양한 동물 적혈구의 세포 표면 당쇄 차이를 쉽게 관찰할 수 있습니다.
On Cellular Glycans, 세포표면의 글리칸
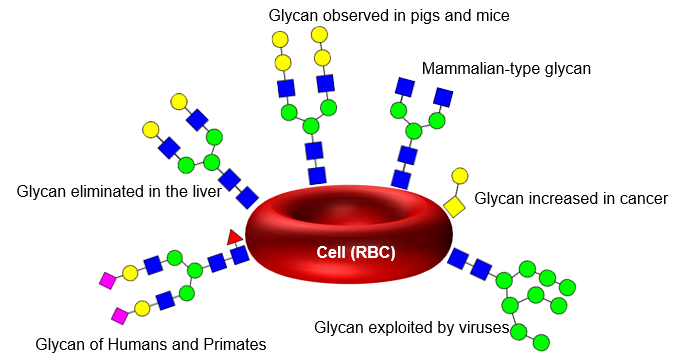
- The surface of cells is covered with various glycans.
- They exist as glycoproteins, glycolipids, and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs).
- The structures vary depending on the species.
- The surface glycans differ depending on the type of cell.
- Glycan structures change due to diseases.
- They play a role in cell-to-cell communication signaling.
- 세포 표면에는 다양한 당쇄(glycan)가 존재
- 당쇄는 당단백질(glycoprotein), 당지질(glycolipid), 당글리코사미노글리칸(GAG, glycosaminoglycan) 형태로 존재
- 당쇄 구조는 생물 종(species)에 따라 다름
- 세포 유형(cell type)에 따라 표면 당쇄 구조가 다름
- 질병 상태에 따라 당쇄 구조가 변화 가능
- 당쇄는 세포 간 신호전달(cell-to-cell communication signaling)에서 중요한 역할을 담당
Diverse Glycan Structures (Examples),다양한 글리칸 구조 (예시)
Comparison of Hemagglutination Activity, 적혈구 응집 활성 비교
Prepare a 2-fold PBS dilution series (25 μL) of each lectin solution in a 96-well plate. After washing the animal preserved blood from Japan Bioserum Co., Ltd. three times with PBS at 5-10 fold the volume, adjust the red blood cells to 2% (v/v) in PBS. Add 50 μL of the red blood cell suspension to each well and incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes before observation.
각 렉틴 용액을 2배 PBS 희석(25 μL)하여 96-well 플레이트에 분주합니다. 일본 Bioserum Co., Ltd.에서 공급한 보존 동물 혈액을 준비합니다. 적혈구를 PBS(5~10배 부피)로 3회 세척한 후, 2% (v/v)로 조정합니다. 적혈구 현탁액(50 μL)을 각 well에 첨가한 후, 실온에서 30분간 반응시킵니다.반응 후, 적혈구 응집 여부를 관찰합니다.
|
Related Product Category Page
|
Carbohydrate-binding Specificity of Lectins, Lectin-Biotin Conjugates, 、Lectin-Agarose (LecBeads) are as follows:
|
Related Product Spotlight Page
|
|
Product Brochures
|
'TCI > Key Visual' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 공유 결합 유기 프레임워크(COFs) 링커, Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) Linkers (1) | 2025.05.13 |
|---|---|
| TCI 포도당 정량 키트(Glucose Measurement Kit) (0) | 2025.05.13 |


