|
About "Lectin"
|
[Discovery, 발견]
In 1888, Peter Hermann Stillmark of Estonia discovered a protein component (hemagglutinin) that agglutinates red blood cells from the seeds of the plant castor bean (Ricinus communis), and this molecule was named "ricin".1) In the early 1900s, Japanese Hideyo Noguchi also found lectins in the venom of pit vipers and discovered limulin as an invertebrate lectin from horseshoe crabs.2,3)
1888년, 에스토니아의 Peter Hermann Stillmark는 피마자(Ricinus communis) 씨앗에서 적혈구를 응집시키는 단백질 성분(혈구응집소, hemagglutinin)을 발견하였으며, 이 분자를 리신(ricin)이라 명명하였습니다. 1900년대 초반, 일본의 노구치 히데요(Hideyo Noguchi)는 살무사(pit viper)의 독에서 렉틴(lectin)을 발견하였으며, 투구게(horseshoe crab)에서 무척추동물 렉틴인 리물린(limulin)을 발견하였습니다.
[Nomenclature, 명명법]
The term "lectin" was coined in 1954 by William C. Boyd and Elizabeth Shapleigh, based on the Latin words "lego/legere" (to read, choose, or gather) and the suffix "-in", which denotes proteins, to describe substances from plants that show blood group-specific agglutination of red blood cells.4)
"렉틴(lectin)"이라는 용어는 1954년 William C. Boyd와 Elizabeth Shapleigh에 의해 처음 명명되었습니다. 이는 라틴어 lego/legere (읽다, 선택하다, 모으다)와 단백질을 의미하는 접미사 -in이 결합된 형태로, 식물 유래 물질 중 혈액형 특이적 적혈구 응집 활성을 나타내는 물질을 의미합니다.
[Definition, 정의]
In 1980, Irwin J. Goldstein, R. Colin Hughes, Michel Monsigny, Toshiaki Osawa, and Nathan Sharon defined lectins as "carbohydrate-binding proteins that have the ability to agglutinate cells or precipitate polysaccharides and glycoproteins, and are not immune response products (antibodies)".5)
While some lectins cannot agglutinate cells due to a lack of multivalent binding sites, other molecules, such as glycosyltransferases, glycosidases, carbohydrate-related transporters and kinases, can agglutinate cells. In 1981, Jan Kocourek and Václav Hořejší proposed a broader definition of lectins as "carbohydrate-binding proteins that do not modify the sugars they bind to".6,7) Lectins are often classified based on carbohydrate-binding specificity or gene family, reflecting species differences and a wide range of functions.8)
1980년, Irwin J. Goldstein, R. Colin Hughes, Michel Monsigny, Toshiaki Osawa, Nathan Sharon은 렉틴을 "세포를 응집시키거나 다당류 및 당단백질을 침전시키는 능력을 가지며, 면역반응 산물(항체)이 아닌 탄수화물-결합 단백질" 과 같이 정의하였습니다. 다만, 일부 렉틴은 다가 결합 부위(multivalent binding site)가 없어 세포 응집이 일어나지 않을 수 있으며, 반면 당전이효소(glycosyltransferase), 당가수분해효소(glycosidase), 탄수화물 관련 수송체 및 키나아제 등의 다른 분자들은 세포 응집 기능을 가질 수도 있습니다. 이에 따라, 1981년 Jan Kocourek과 Václav Hořejší는 기존 정의를 확장하여 렉틴을 "렉틴은 결합하는 당을 변형시키지 않는 탄수화물-결합 단백질"과 같이 재정의하였습니다. 렉틴은 탄수화물 결합 특이성 또는 유전자 계통(gene family)에 따라 분류되며, 이는 생물 종(species) 간의 차이와 다양한 기능성을 반영합니다.
[Applications, 응용]
Inspired by the differences in agglutination reactions of red blood cells from different animals toward various lectins, Karl Landsteiner discovered the human ABO-type blood group (glycan antigens) in 1900 and he won the Nobel Prize in 1930.9) Lectins have long been used for analyzing and profiling the distinct surface glycans of different cells. Recently, technologies such as "lectin microarray-based glycan profiling" and "DNA barcode-labeled lectin single-cell glycan analysis" have been developed, making lectins crucial in cutting-edge research on cell surface glycans.10,11)
적혈구 응집 반응의 차이에 대한 연구를 바탕으로, Karl Landsteiner는 1900년 **인간 ABO 혈액형(당항원, glycan antigens)**을 발견하였으며, 1930년 노벨 생리학·의학상을 수상하였습니다.
이후 렉틴은 세포 표면 당쇄(glycan) 분석 및 프로파일링에 지속적으로 활용되어 왔습니다. 최근에는 렉틴을 활용한 렉틴 마이크로어레이 기반 당쇄 프로파일링(lectin microarray-based glycan profiling), DNA 바코드-표지 렉틴 단일세포 당쇄 분석(DNA barcode-labeled lectin single-cell glycan analysis)과 같은 최신 분석 기술이 개발되어, 렉틴이 세포 표면 당쇄 연구의 필수적인 도구로 자리 잡고 있습니다.
|
Products
|
Hemagglutinin Lectin (Recombinant lectins)
R0225 Recombinant Polyporus squamosus lectin (= rPSL1a) expressed in Escherichia coli
R0226 Recombinant Laetiporus sulphureus lectin N-Terminal Domain (= rLSL-N) expressed in Escherichia coli
R0227 Recombinant Marasmius oreades agglutinin (= rMOA) expressed in Escherichia coli
R0228 Recombinant Sclerotium rolfsii lectin (= rSRL) expressed in Escherichia coli
R0229 Recombinant Griffithsia sp. lectin (= rGRFT) expressed in Escherichia coli
L0169 Lectin, Fucose specific (= AOL) from Aspergillus oryzae (5mg/mL, PBS pH6.5)

Product No. R0225, R0226, R0227, R0228, R0229 were commercialized under license from National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Japan.
Product No. L0169 was commercialized under license from GEKKEIKAN SAKE COMPANY, LTD.
|
Applications
|
The differences in the cellular glycans of animal red blood cells can be easily observed with our lectin series.
TCI의 렉틴 시리즈를 사용하면 다양한 동물 적혈구의 세포 표면 당쇄 차이를 쉽게 관찰할 수 있습니다.

On Cellular Glycans, 세포표면의 글리칸
- The surface of cells is covered with various glycans.
- They exist as glycoproteins, glycolipids, and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs).
- The structures vary depending on the species.
- The surface glycans differ depending on the type of cell.
- Glycan structures change due to diseases.
- They play a role in cell-to-cell communication signaling.
- 세포 표면에는 다양한 당쇄(glycan)가 존재
- 당쇄는 당단백질(glycoprotein), 당지질(glycolipid), 당글리코사미노글리칸(GAG, glycosaminoglycan) 형태로 존재
- 당쇄 구조는 생물 종(species)에 따라 다름
- 세포 유형(cell type)에 따라 표면 당쇄 구조가 다름
- 질병 상태에 따라 당쇄 구조가 변화 가능
- 당쇄는 세포 간 신호전달(cell-to-cell communication signaling)에서 중요한 역할을 담당
Diverse Glycan Structures (Examples),다양한 글리칸 구조 (예시)

Comparison of Hemagglutination Activity, 적혈구 응집 활성 비교
Prepare a 2-fold PBS dilution series (25 μL) of each lectin solution in a 96-well plate. After washing the animal preserved blood from Japan Bioserum Co., Ltd. three times with PBS at 5-10 fold the volume, adjust the red blood cells to 2% (v/v) in PBS. Add 50 μL of the red blood cell suspension to each well and incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes before observation.
각 렉틴 용액을 2배 PBS 희석(25 μL)하여 96-well 플레이트에 분주합니다. 일본 Bioserum Co., Ltd.에서 공급한 보존 동물 혈액을 준비합니다. 적혈구를 PBS(5~10배 부피)로 3회 세척한 후, 2% (v/v)로 조정합니다. 적혈구 현탁액(50 μL)을 각 well에 첨가한 후, 실온에서 30분간 반응시킵니다.반응 후, 적혈구 응집 여부를 관찰합니다.

|
Related Product Category Page
|
Carbohydrate-binding Specificity of Lectins, Lectin-Biotin Conjugates, 、Lectin-Agarose (LecBeads) are as follows:
|
Related Product Spotlight Page
|
|
Product Brochures
|
'TCI > Key Visual' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 공유 결합 유기 프레임워크(COFs) 링커, Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) Linkers (1) | 2025.05.13 |
|---|---|
| TCI 포도당 정량 키트(Glucose Measurement Kit) (0) | 2025.05.13 |
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are crystalline organic frameworks consisting of a network structure made of covalent bonds.1,2) COFs are classified as porous crystalline materials similar to metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)/porous coordination polymers (PCPs) and zeolites. They include 2D COFs, which are constructed by stacking layers of 2D covalently bonded sheets, and 3D COFs, which are constructed by 3D connected frameworks. COFs are expected to be used as molecular storage or separation materials, catalysts, electronic materials, energy storage materials, battery materials, and drug delivery materials, due to their porosity, crystallinity, and structural diversity.
COFs are designed and synthesized by combining monomers, also called linkers, according to intended topology. TCI has more than 70 linkers in stock, and we are constantly adding new items to our catalog. Common linkers are shown below by functional groups.
코발렌트 유기 골격체(COFs)는 공유 결합으로 이루어진 네트워크 구조를 가진 결정성 유기 골격체입니다.1,2) COF는 금속-유기 골격체(MOFs)/유기 금속 착물(PCPs)과 제올라이트와 유사한 다공성 결정성 물질로 분류됩니다. COF는 2D COF와 3D COF로 나눌 수 있습니다. 2D COF는 2D로 결합된 시트들을 쌓아서 구성된 구조이고, 3D COF는 3D로 연결된 골격체로 구성됩니다. COF는 다공성, 결정성, 구조적 다양성 덕분에 분자 저장 또는 분리 물질, 촉매, 전자 재료, 에너지 저장 재료, 배터리 재료, 약물 전달 재료 등으로 사용될 것으로 기대됩니다.
COF는 의도된 토폴로지에 맞게 모노머, 즉 링커를 결합하여 설계하고 합성합니다. TCI는 70종 이상의 링커를 보유하고 있으며, 새로운 항목을 계속해서 카탈로그에 추가하고 있습니다. 일반적인 링커들은 아래와 같이 기능성 그룹에 따라 분류됩니다.
|
Aldehyde Linkers
|
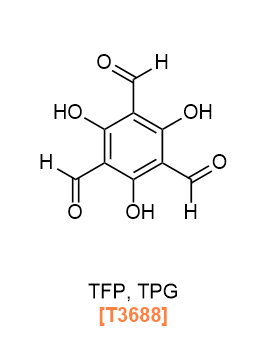
A type of COFs based on imine linkage, synthesized by condensation of aldehydes and amines, was first reported in 2009,3) and imine-based COFs have become the most widely reported COFs. One of the advantage of imine based COFs is their higher chemical stability compared to boroxines and boronate esters. In addition, a number of researchers have reported post-synthetic modification or functionalization of imine based COFs, e.g., COFs for CO2 capture were synthesized by post-synthetic modification and functionalization of imine-based structures.4) In 2012, β-ketoenamine-type COFs synthesized by using 2,4,6-triformylphloroglucinol (TPG, TFP) as an aldehyde linker were reported,5) and have recently attracted much attention because of their stability towards acids and bases.
이민 결합을 기반으로 하는 COF의 한 유형은 알데히드와 아민의 축합 반응을 통해 합성되었으며, 2009년에 처음 보고되었습니다.3) 이민 기반 COF는 가장 널리 보고된 COF 유형이 되었습니다. 이민 기반 COF의 장점 중 하나는 보로신(boroxines)과 보로네이트 에스터(boronate esters)에 비해 더 높은 화학적 안정성을 가진다는 점입니다. 또한, 많은 연구자들이 이민 기반 COF의 후합성 수정(post-synthetic modification) 또는 기능화(functionalization)를 보고하였습니다. 예를 들어, CO2 포집을 위한 COF는 이민 기반 구조의 후합성 수정과 기능화를 통해 합성되었습니다.4) 2012년에는 2,4,6-트리포르밀플로로글루시놀(TPG, TFP)을 알데히드 링커로 사용하여 합성한 β-케토에나민(β-ketoenamine)형 COF가 보고되었으며,5) 최근에는 산과 염기에도 안정성이 있어 많은 주목을 받고 있습니다.











Products
T0010 Terephthalaldehyde (= PDA)
B2854 4,4'-Biphenyldicarboxaldehyde
B6576 [2,2'-Bipyridine]-5,5'-dicarbaldehyde
D6103 2,3-Dihydroxyterephthalaldehyde
D5510 2,5-Dihydroxyterephthalaldehyde
D6056 2,5-Dimethoxyterephthalaldehyde
T4088 2,3,5,6-Tetrafluoroterephthalaldehyde
T3688 2,4,6-Triformylphloroglucinol (= TFP, TPG)
D6046 2,4,6-Triformylresorcinol
F1252 1,3,5-Tris(4-formylphenyl)benzene
T4078 4,4',4''-(1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triyl)tribenzaldehyde
T4077 2,4,6-Tris(4-formylphenoxy)-1,3,5-triazine
|
Amine Linkers
|
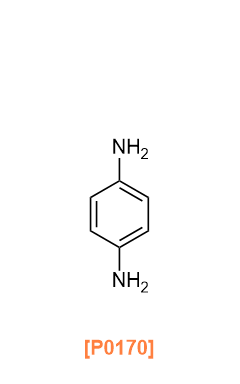
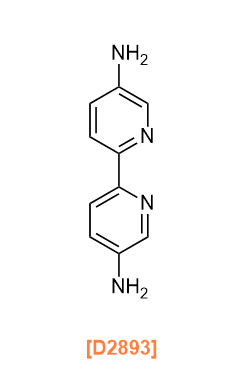
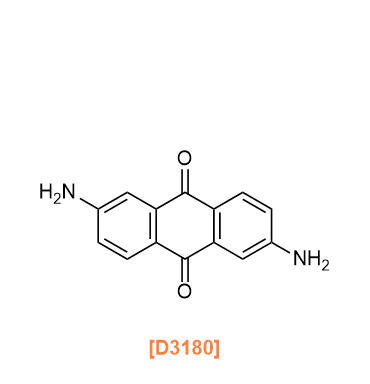
Amine linkers are used to synthesize imine-linked COFs by condensation of aldehydes and amines as described in the aldehyde linkers section, as well as imide-linked COFs mentioned in the carboxylic anhydride linkers section below, and squaraine-linked COFs.6)
아민 링커는 알데히드 링커 섹션에서 설명한 대로 알데히드와 아민의 축합 반응을 통해 이민 결합 COF를 합성하는 데 사용되며, 또한 아래의 카르복실산 무수물 링커 섹션에서 언급된 이미드 결합 COF와 스쿠아레인 결합 COF를 합성하는 데에도 사용됩니다.6)



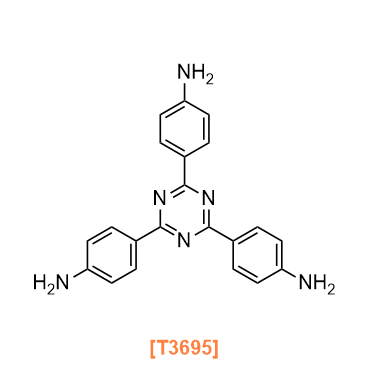



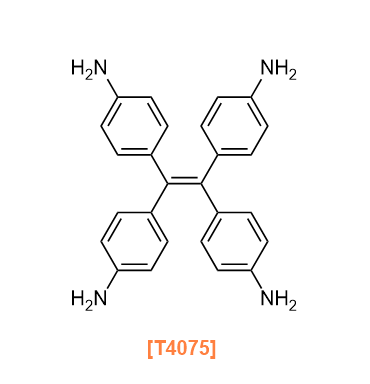
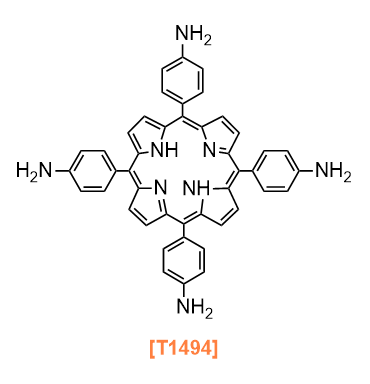
Products
D2893 [2,2'-Bipyridine]-5,5'-diamine
D3180 2,6-Diaminoanthraquinone
B6846 4,4'-(Benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-4,7-diyl)dianiline
T2332 Tris(4-aminophenyl)amine (= TAPA)
T2728 1,3,5-Tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene (= TAPB)
T3695 4,4',4''-(1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triyl)trianiline
T4341 4',4''',4'''''-(1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triyl)tris[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-amine)]
M3538 2,5,8-Triamino-1,3,4,6,7,9,9b-heptaazaphenalene
T2947 Tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)methane
T4075 Tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)ethylene
T1494 5,10,15,20-Tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)porphyrin
|
Carboxylic Anhydride Linkers
|
Imide-linked COFs obtained by condensation of carboxylic anhydrides and amines have also been reported7) and are expected to be applied to battery materials8) and CO2 capture materials.9)
카르복실산 무수물과 아민의 축합 반응을 통해 얻어진 이미드 결합 COF도 보고된 바 있으며,7) 이는 배터리 재료8) 및 CO2 포집 재료9) 등에 적용될 것으로 예상됩니다.



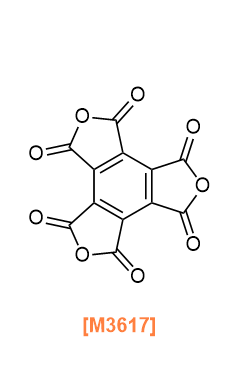

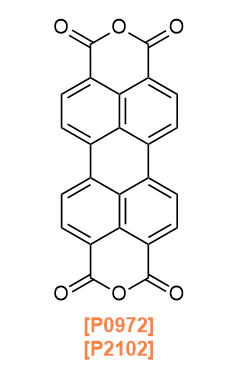
Products
B0040 Pyromellitic Dianhydride
P2103 Pyromellitic Dianhydride (purified by sublimation)
N1128 2,3,6,7-Naphthalenetetracarboxylic 2,3:6,7-Dianhydride
N0369 Naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetracarboxylic Dianhydride
N0755 Naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetracarboxylic Dianhydride (purified by sublimation)
N1247 1,2,5,6-Naphthalenetetracarboxylic Dianhydride
P0972 3,4,9,10-Perylenetetracarboxylic Dianhydride
P2102 3,4,9,10-Perylenetetracarboxylic Dianhydride (purified by sublimation)
|
Boronic Acid Linkers
|
The self-condensation of boronic acids to produce boroxines and the condensation of boronic acids and catechols to produce boronic esters are the first synthetic strategies to synthesize COFs.10)
보로닉산의 자기 축합 반응을 통해 보로신을 생성하고, 보로닉산과 카테콜의 축합 반응을 통해 보로네이트 에스터를 생성하는 것이 COF 합성을 위한 첫 번째 합성 전략입니다.10)


|
Other Linkers
|
COFs can also be constructed with linkers beyond imines, imides, and boroxines. COFs prepared using linkers other than amines, aldehydes, carboxylic anhydrides, and boronic acids could include those utilizing hydrazones, azines, C=C double bonds, etc.
For example:
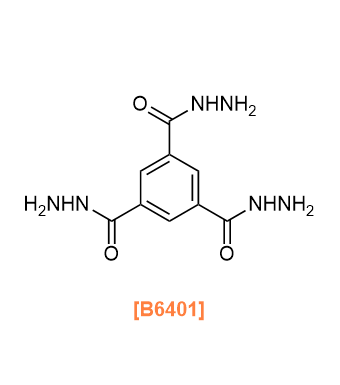
- Hydrazone-type COFs synthesized with hydrazides and aldehydes, are known for their structural flexibility and significant potential for post-synthetic modifications.11,12,13)
- Ionic COFs synthesized using 1,2,3-triaminoguanidinium chloride, where the triaminoguanidinium cation reacts with an aromatic aldehyde to form the covalent linkages within the framework.14)
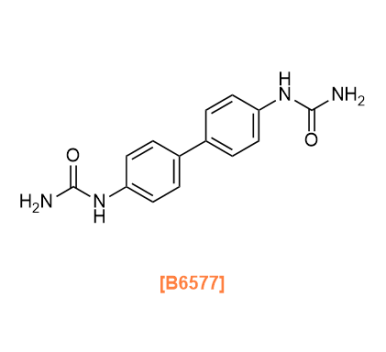
- β-ketoenamine-type COFs can also be derived by synthesizing precursors with urea linkage. After the precursor with highly-reversible urea linkages is formed, the "reconstruction" process transforms it into the final β-ketoenamine COF. Researchers can achieve a significantly higher crystallinity and surface area in the final β-ketoenamine COF by using this "precursor approach" with urea linkages.15)
COF는 이민, 이미드, 보로신 외에도 다른 링커를 사용하여 합성할 수 있습니다. 아민, 알데히드, 카르복실산 무수물, 보로닉산 이외의 링커를 사용하여 합성한 COF에는 하이드라존, 아진, C=C 이중 결합 등을 이용한 COF가 포함될 수 있습니다.
예:
1. 하이드라존-형 COF는 하이드라자이드와 알데히드를 사용하여 합성되며, 구조적 유연성 및 후합성 수정 가능성으로 잘 알려져 있습니다.11,12,13)
2. 이온성 COF는 1,2,3-트리아미노구아니디늄 염화물(1,2,3-triaminoguanidinium chloride)을 사용하여 합성됩니다. 여기서 트리아미노구아니디늄 양이온은 방향족 알데히드와 반응하여 골격 내에서 공유 결합을 형성합니다.14)
3. β-케토에나민형 COF는 요소 결합을 사용하여 전구체를 합성하여 얻을 수 있습니다. 고도로 가역적인 요소 결합을 가진 전구체가 형성된 후, "재구성" 과정을 통해 최종적인 β-케토에나민 COF로 변환됩니다. 이 "전구체 접근법"을 사용하면 최종 β-케토에나민 COF에서 훨씬 높은 결정성과 표면적을 얻을 수 있습니다.15)







Products
H0907 2,3,6,7,10,11-Hexahydroxytriphenylene (= HHTP)
B6577 1,1'-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4,4'-diyl)diurea
T0758 Terephthalic Dihydrazide
H0172 Hydrazine MonohydrateH0697Hydrazine Anhydrous
T4080 1,2,3-Triaminoguanidinium Chloride
C0460 2,4,6-Trichloro-1,3,5-triazine
T4145 2,5,8-Trichloro-1,3,4,6,7,9,9b-heptaazaphenalene
X0061 1,4-PhenylenediacetonitrileT0016Terephthalonitrile
|
Related Products
|
The following is a list of common reagents that are used as modulators to increase the crystallinity of the resulting COFs and as catalysts for the synthesis of COFs.
다음은 결과적으로 형성되는 COF의 결정성을 증가시키기 위한 조절제로 사용되며, COF 합성의 촉매로 사용되는 일반적인 시약들의 목록입니다.
Modulators
B0739 4-tert-Butylpyrocatechol
Catalysts
A2035 Acetic AcidT1663Scandium(III) Triflate
|
Examples of COFs Synthesis
|
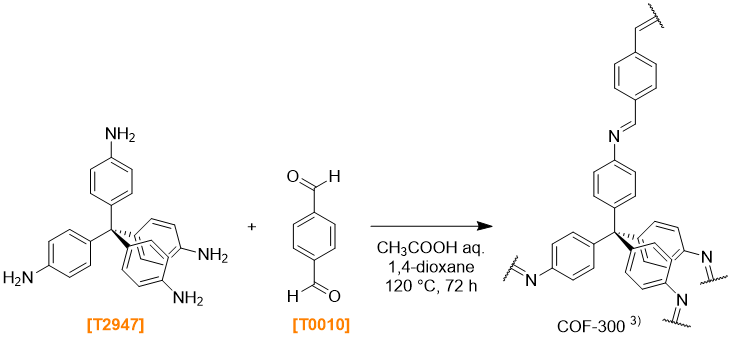
Synthesis of COF-300 3)
Synthesis of TpPa-1 5)

Synthesis of COF-1 10)

Synthesis of Bth-Dma COF 13)

Synthesis of RC-COF-3 15)

|
Related Product Category Pages
|
|
Product Brochures
|
Covalent Organic Framework (COF) Linkers (PDF file)
Aldehyde Linkers for β-Ketoenamine Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) (PDF file)
Raw Material for Polyimides and COFs Mellitic Trianhydride (PDF file)
2,2'-Bipyridine Linkers for the Synthesis of COFs (PDF file)
Diurea Linkers for the Synthesis of Reconstructed COFs (PDF file)
Hydrazide Linkers for Covalent Organic Flameworks (COFs) (PDF file)
'TCI > Key Visual' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Hemagglutinin Lectin, 헤마글루티닌 렉틴 (0) | 2025.05.13 |
|---|---|
| TCI 포도당 정량 키트(Glucose Measurement Kit) (0) | 2025.05.13 |
Living organisms utilize glucose as their primary source of energy, making it an important metabolic indicator, especially in the study of sugars and lipids. Additionally, cancer cells are known to consume an elevated amount of glucose compared to normal cells, making it equally important in the study of cancer metabolism. Our Glucose Measurement Kit can accurately measure the concentration of glucose in samples such as serum samples and cell culture supernatants.
생물체는 포도당을 주요 에너지원으로 사용하며, 이는 당과 지질 대사 연구에서 중요한 대사 지표로 작용합니다. 또한, 암세포는 정상 세포보다 더 많은 포도당을 소비하는 것으로 알려져 있어, 암 대사 연구에서도 포도당의 중요성이 강조됩니다. 본 포도당 정량 키트(Glucose Measurement Kit)는 혈청 및 세포 배양 상등액 등의 시료에서 포도당 농도를 정확하게 측정할 수 있습니다.

Example of use of Glucose Measurement Kit (Product No. G0656)
|
Product
|
|
Kit Components
|
- Glucose Measurement Solution 2 vials
- Glucose Standard Solution (500 mg/dL) 2 vials
|
Volume
|
- Enough for 200 tests (100 tests x2)
|
Advantages
|
· Allows for the measurement of glucose concentrations down to as low as 50 mg/dL and as high as 500 mg/dL.
· Contains two batches of reagents for the analysis of 2 separate batches.
· Allows for the measurement of glucose in blood and cell culture supernatants.
· Quantify glucose concentration through a simple absorbance measurement at 542 nm.
· Ascorbate oxidase is included in the glucose measurement solution, reducing the effect of ascorbic acid in the sample.
- 최소 50 mg/dL에서 최대 500 mg/dL까지 포도당 농도를 측정 가능
- 2개의 시약 배치 포함, 서로 다른 2개의 실험 세트에서 사용 가능
- 혈액 및 세포 배양 상등액 내 포도당 농도 측정 가능
- 흡광도 측정을 통한 정량 분석 가능 (파장: 542 nm)
- 아스코르브산 산화효소(Ascorbate oxidase) 포함, 시료 내 아스코르브산(비타민 C)의 간섭 효과를 줄임
|
Application: Determination of Glucose Concentration in Bovine Serum Using G0656
|
1. Dilute Glucose Standard Solution (500 mg/dL) with deionized water to prepare a 2-fold dilution series of glucose (100 μL each).
2. Transfer 2 μL of each glucose dilution series solution into a 96-well plate. Additionally transfer 2 μL of bovine serum sample as a sample into same 96-well plate.
3. Add 200 μL of Glucose Measurement Solution to each well and incubated plate at room temperature for 20 minutes.
4. After 20 minutes, measure the absorbance at 540 (10) nm.
5. Create a calibration curve from the glucose dilution series data and use it to calculate the concentration of glucose in the bovine serum.
1. 포도당 표준 용액(500 mg/dL)을 초순수로 희석하여 2배 단계 희석(2-fold dilution) 시리즈를 준비 (각 100 μL).
2. 각 포도당 희석 용액 2 μL 및 우혈청 시료 2 μL를 96 well plate에 분주.
3. 각 well에 포도당 측정 시약 200 μL를 추가한 후 실온에서 20분간 반응.
4. 20분 후 540(10) nm에서 흡광도 측정.
5. 포도당 표준곡선 데이터를 이용하여 우혈청 내 포도당 농도 계산.

Figure. Glucose Standard Curve Concentrations and Associated Absorbance Measurements
The absorbance of bovine serum at 540 nm was determined to be 0.1717. After comparison with the standard curve, the corresponding glucose concentration was found to be 60.65 mg/dL = 606.5 mg/L.
우혈청의 540 nm에서 흡광도 값: 0.1717, 표준 곡선과 비교하여 산출된 포도당 농도: 60.65 mg/dL (606.5 mg/L)
|
Product Brochure
|
|
Related Product Brochure Category
|
'TCI > Key Visual' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Hemagglutinin Lectin, 헤마글루티닌 렉틴 (0) | 2025.05.13 |
|---|---|
| 공유 결합 유기 프레임워크(COFs) 링커, Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) Linkers (1) | 2025.05.13 |








